Introduction
2025年2月20号Qwen团队发布了Qwen2.5 VL技术报告,Qwen2.5 VL包括3B,7B, 72B三个size。Qwen2.5-VL主要在架构,数据上进行了改进。通过评测,Qwen2.5-VL在多个benchmark上取得了SOTA。
Qwen2.5 VL认为已有模型的缺点为:
- 计算复杂度高
- 上下文理解能力有限
- 细粒度visual perception能力不足
- 在不同上下文长度下表现不一致
Qwen2.5 VL的贡献为:
- 使用了一个从零开始训练的ViT作为vision encoder,并且在ViT中使用了window attention,来提高计算效率
- 使用了dynamic FPS sampling,用于处理不同采样率的视频输入
- 将MRoPE扩展到了temporal domain上,进一步提高了模型在与时间相关任务上的表现
- 使用了更高质量的数据集,其中预训练阶段使用了4.1T的token
Qwen2.5 VL的主要亮点为:
- 优秀的document parsing能力
- 精确的object grounding能力
- 针对长视频的理解和细粒度grounding能力
- 针对UI的agent functionality
模型架构
总览
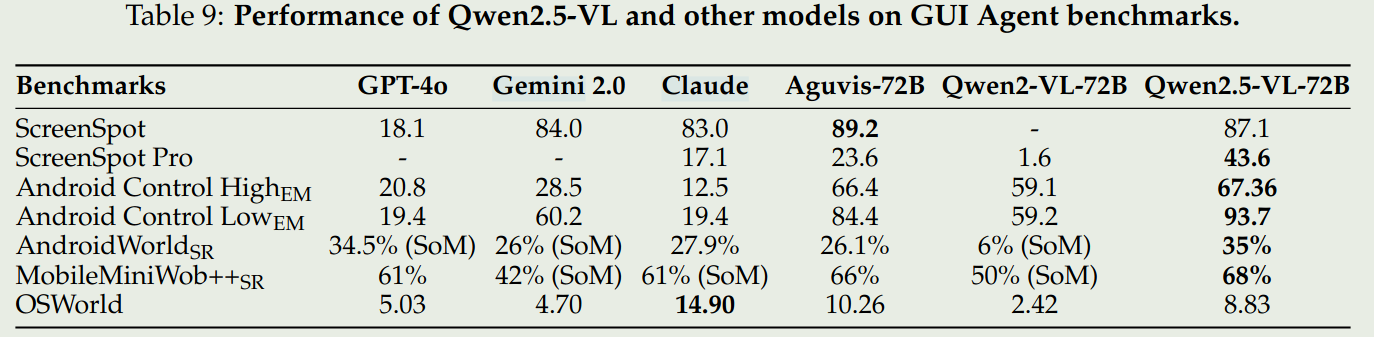
Qwen2.5 VL和Qwen2 VL的架构基本一致,包括Vision Encoder,Language Encoder,以及projector layer三个部分,其架构图如下:
- LLM: 使用Qwen2.5 LLM作为LLM,并且将1D-RoPE升级为了MRoPE
- Vision Encoder: 使用一个从零开始训练的ViT架构,patch_size为14,position embedding为2D-RoPE, attention为window attention和self-attention的混合,其中,只有四层使用的是self-attention.对于输入的图片,ViT会将图片resize到28的整数倍。
- Projector Layer: 使用的是一个两层的MLP
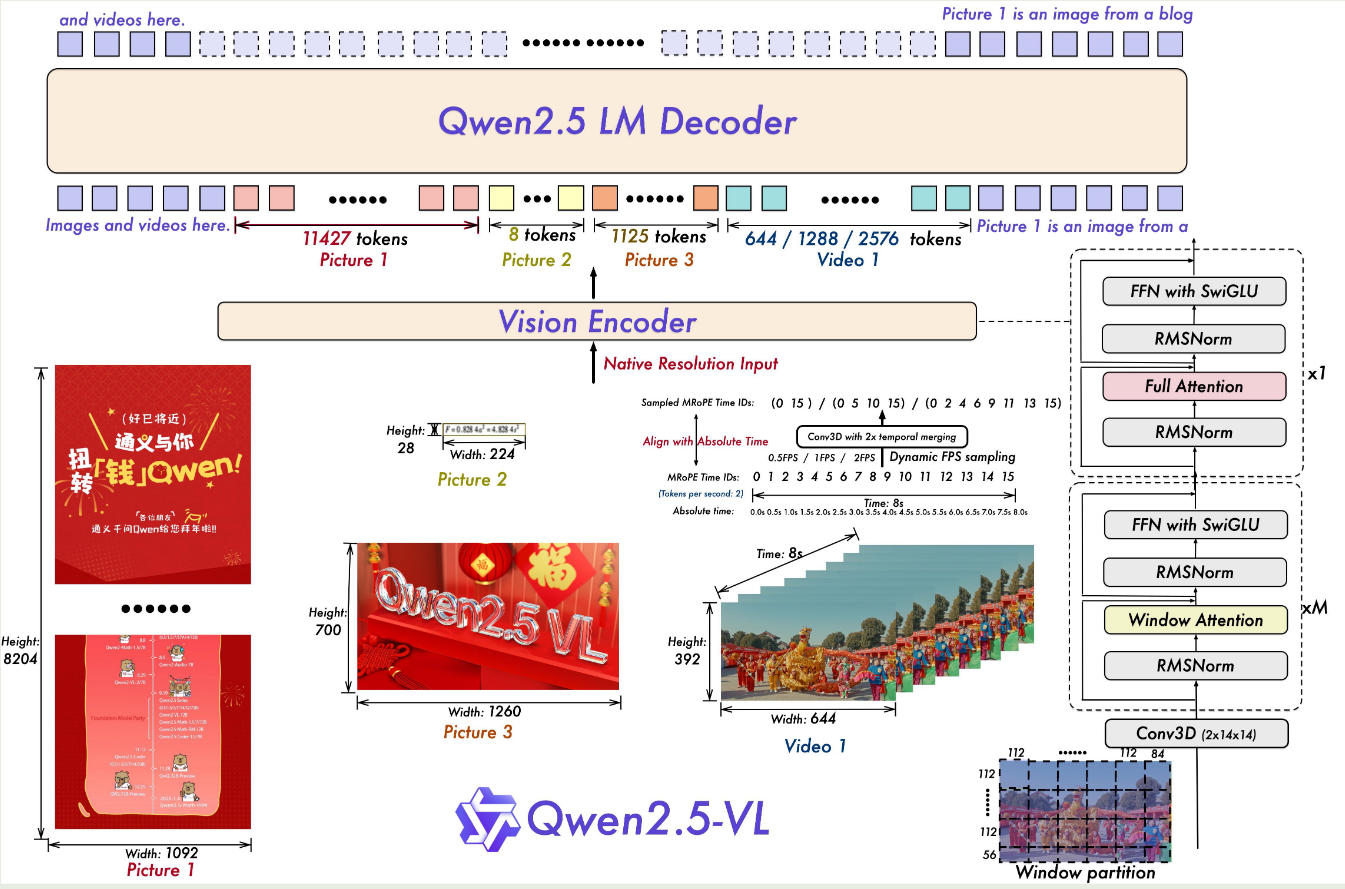
模型的参数配置如下图
Vision Encoder
Vision encoder的主要改进点为:
- 使用了window attention来提升计算效率,window attention的size为 $112\times 112$, 对应为 $8\times 8$ 个patch. 这样做的好处是可以不用对图片做scaling
- 使用了2D RoPE来捕捉空间信息,使用3D RoPE来捕捉视频输入的时间信息
- 与LLM的结构进行对齐,包括使用RMSNorm替换LayerNorm,使用SwiGLU替换ReLU
输入处理
对于图片输入,Qwen2.5 VL使用原始图片的空间信息来构建坐标,而不是将坐标normalize到[0, 1000]之间,这样让模型可以处理不同精度的图片输入。
对于视频输入,因为使用了3D RoPE,因此Qwen2.5 VL可以处理不同帧率的视频输入,这样就避免了不同帧率视频对模型视频理解带来的影响。这一点和Apollo里的想法是一样的。具体来说,Qwen2.5 VL首先将连续的两帧group到了一起,然后使用了temporal ID来将position和视频所对应的时间进行对齐。这里可以看Qwen2.5 VL的代码:
| |
这里fps为1,表示每一帧对应一秒,tokens_per_second为25,表示每秒包含25个token,temporal_patch_size为2,表示每个temporal patch包含2个frame。因此一个patch里面,就包含了2frame, 对应50tokens. 然后前面提到连续两帧会被group到一起,因此每个temporal patch对应4个spatial patches. 其position_ids为:
| |
训练
预训练
数据
预训练阶段使用了4.1T的token,包括image captions, interleaved image-text data, optical character recognition (OCR) data, visual knowledge (e.g., celebrity, landmark, flora, and fauna identification), multi-modal academic questions, localization data, document parsing data, video descriptions, video localization, and agent-based interaction data. 作者详细介绍了以下几种数据:
- Interleaved image-text data: 主要1. 提高模型的上下文学习能力;2. 保持模型的text-only能力;3.包含一些通用信息。数据清洗包括:1. 基于text-only quality过滤; 2. 基于image-text相关性过滤;3. 基于image-text互补程度过滤;4.基于information density balance过滤.
- Grounding data:作者使用了Grounding DINO, SAM等模型来生成一些grounding data.为了提升模型在open-vocabulary detection上的能力,作者将训练数据集扩展到了1万个object category上,作者还使用了一些point-based object grounding data来提升模型的能力
- Document Parsing data:作者基于text,image, music sheets和chemical formulas合成了一些HTML格式的数据,然后根据tag和bounding box来提升模型document parsing的能力
- OCR data:作者使用了开源,合成和in-house的数据集,数据集主要提到multi-lingual以及1M的chart-type数据
- Video data:作者通过pipeline构建了long video caption来提升模型长视频的理解能力
- Agent data:作者收集了一些mobile device和网页的screenshots,然后基于agent框架来合成控制轨迹
训练
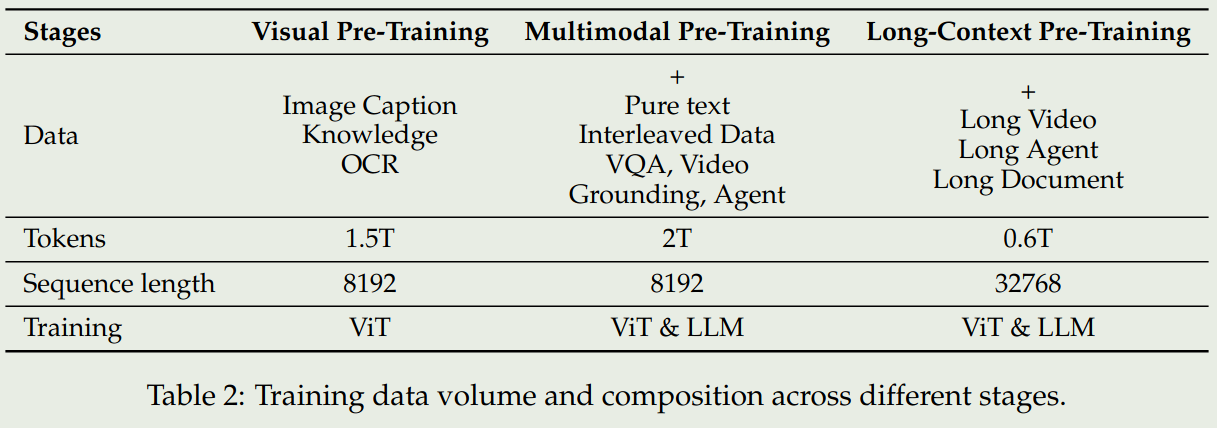
如上图所示,Qwen2.5 VL的预训练阶段包括了三个阶段:
- Visual Pretraining:这一阶段使用了image-caption, knowledge, OCR数据集,旨在提升ViT提取视觉特征的能力
- multimodal pretraining:这一阶段在第一阶段的基础上增加了pure-text, interleaved data, VQA, Video grounding, agent data, 旨在提升模型处理复杂视觉信息的能力
- long-context pretraining: 这一阶段,在第二阶段的基础上,增加了long video, long agent, long document data,旨在提升模型处理长上下文的能力
后训练
数据
SFT阶段使用大概2M的样本进行训练,其中纯文本和多模态数据占比为1:1,语言主要是中文和英文。
为了保证数据质量,作者提供了一个数据清洗的pipeline,包括:
- domain-specific categorization: 作者基于Qwen2-VL-72B构建了Qwen2-VL-Instag,用于将QA pair分为8个大类别,30个小类别
- Domain-tailed filtering:作者使用了rule-based和model-based方法来提升数据的质量
- rule-based filtering: 重复性检测,格式检测等
- model-based filtering: 使用基于Qwen2.5-VL训练的reward model来从多个维度评估QA pair的质量
为了进一步提升模型的推理能力,作者还是用了rejection sampling来refine 数据集。
训练
post-training阶段分为SFT和DPO两个小阶段,这个阶段都会冻结VIT. SFT阶段使用大多数的训练数据,而DPO阶段专注于image-text data和pure text data,以更好地进行对齐。具体做法就是基于Grounding truth,使用checkpoint来评估数据的质量,然后只保留答案正确的数据来训练。
评测
- 通用VQA
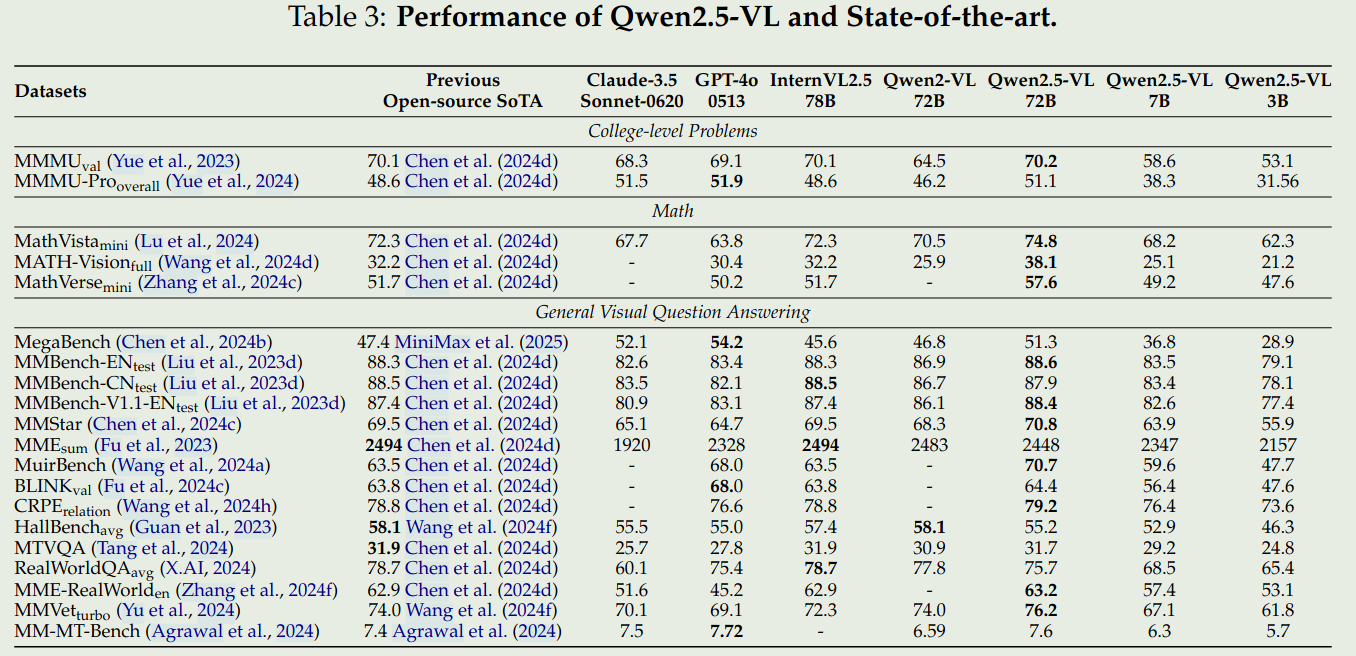
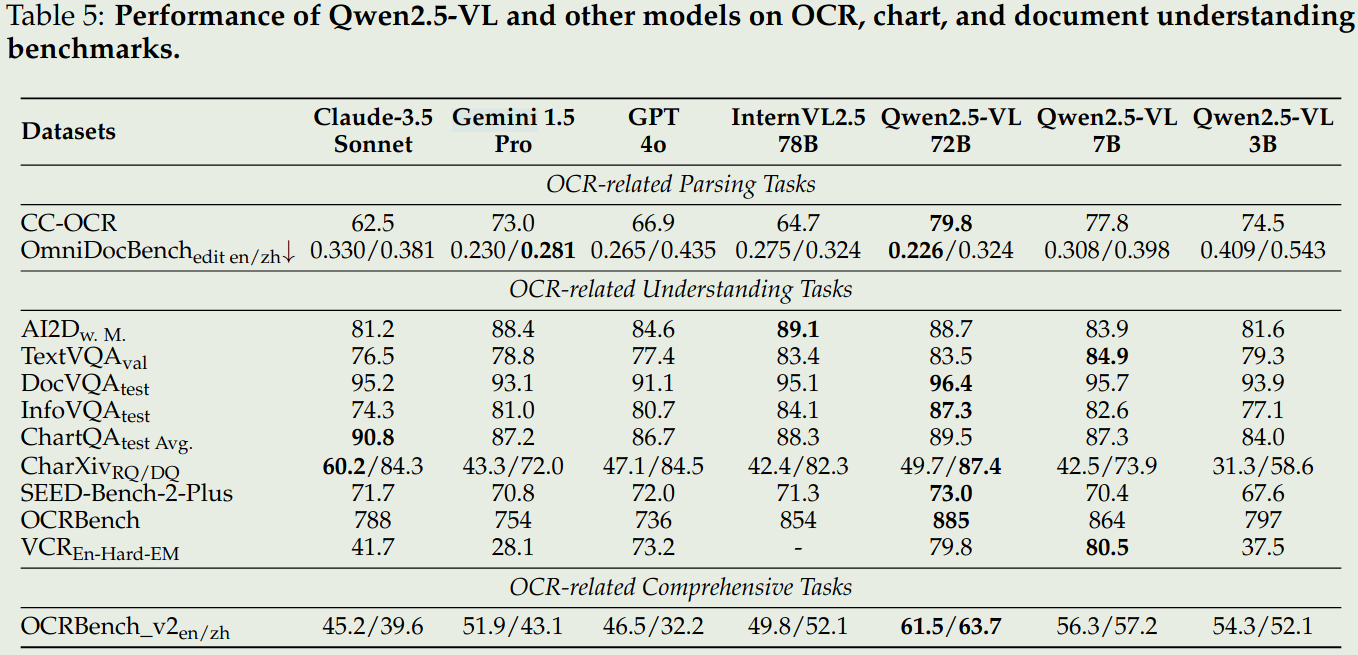
- 文档理解和OCR
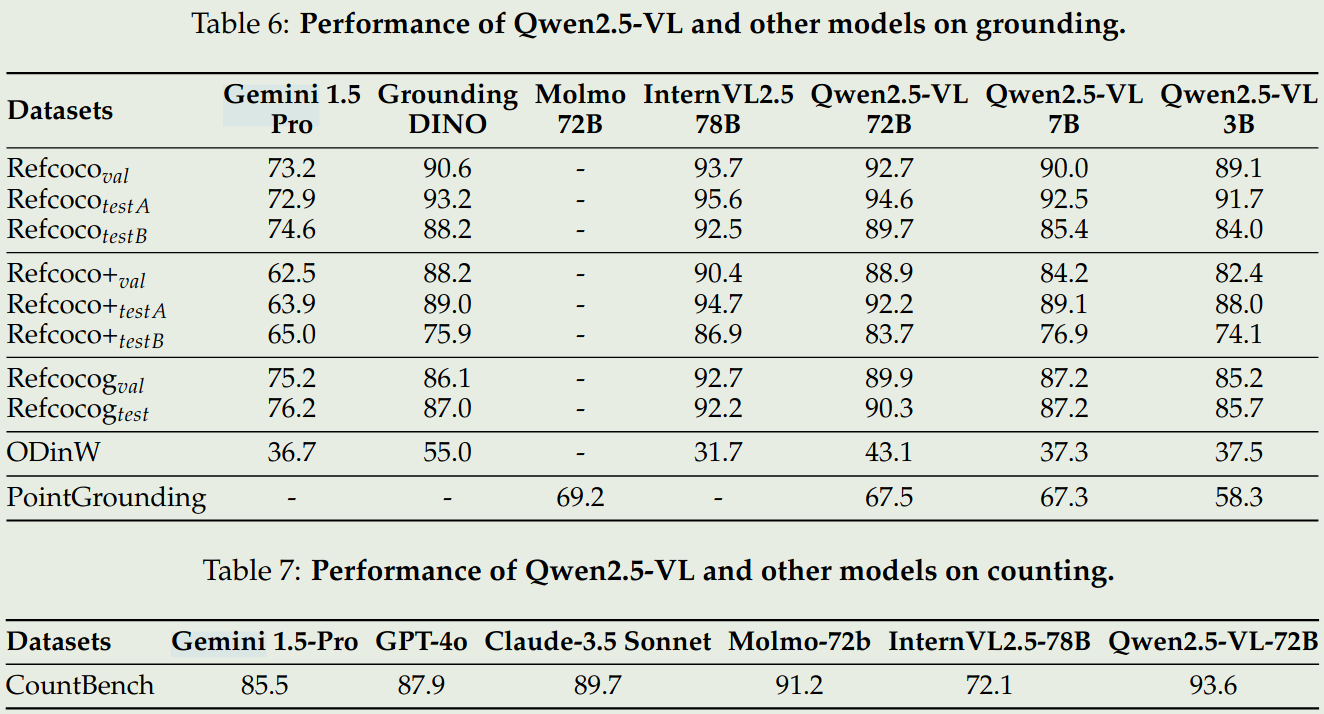
- 空间理解
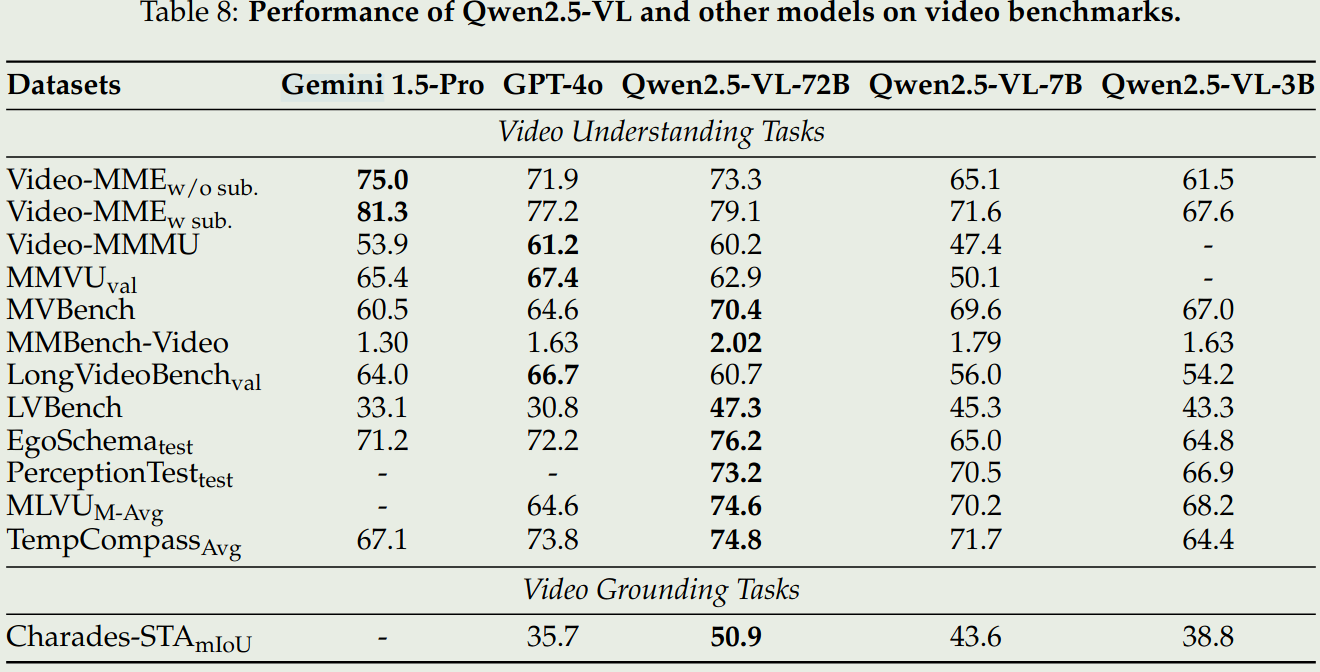
- 视频理解和Grounding
- Agent